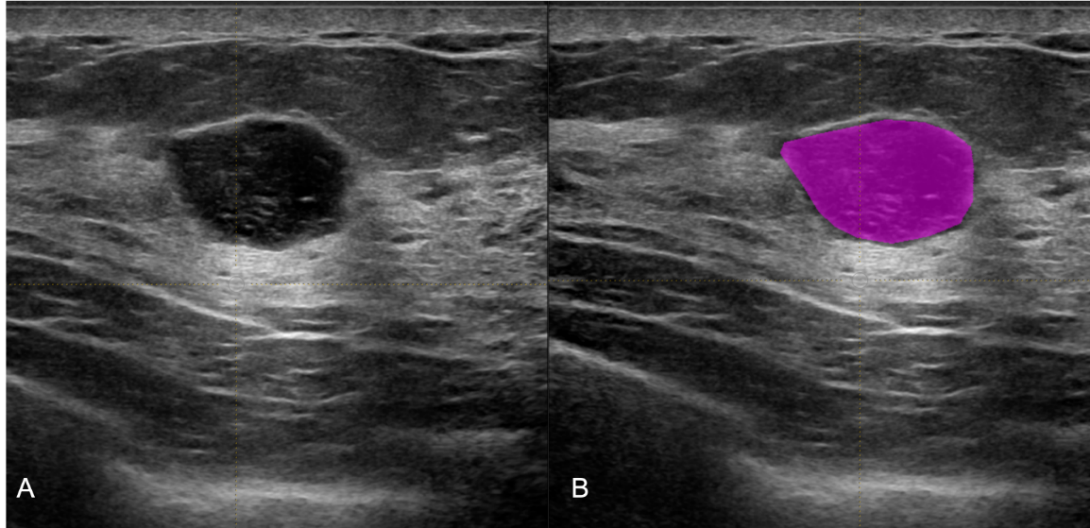
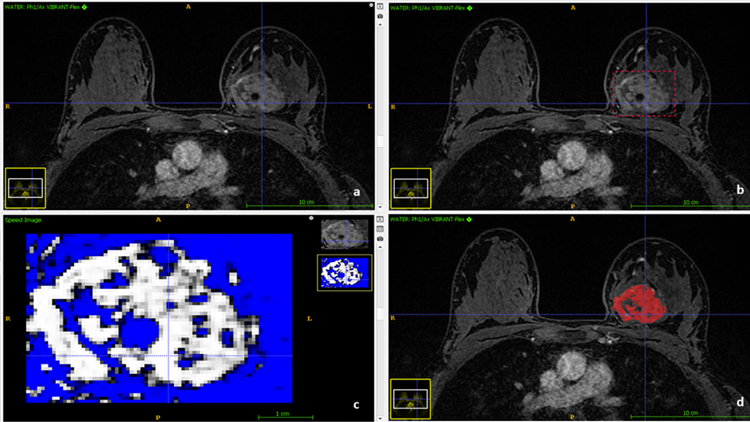
Radiomic and Breast cancer
Breast cancer is the most common non–skin cancer and a leading cause of death by cancer. Although its diagnosis is still based on histopathological confirmation by biopsy, radiomics has gained recognition as a new tool for non-invasively profiling. The ultimate purpose of radiomics should be early diagnosis of breast cancer and prediction of its clinical course and biological aggressiveness in order to optimize treatment. The imaging evaluation of breast cancer through mammography, ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging is currently essentially qualitative, including subjective evaluations of tumour morphology, type of enhancement, and anatomic relationship to the surrounding tissues. However, a quantitative evaluation is demanded too to reach a personalized medicine. Data derived from radiomics investigation may provide valuable information to differentiate benign from malignant lesions, to predict treatment response, to assess cancer molecular profile and to derive robust models that combine multidisciplinary information.